The Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR) recently published its General Comment on the environmental dimension of sustainable development. In addition to recognising human rights defenders, the Comment clarifies State obligations towards marginalized communities and notes the importance of transitioning away from fossil fuels. It also outlines States’ extraterritorial obligations.
ISHR provided two written inputs to the draft of this General Comment earlier this year – a standalone submission regarding the recognition and protection of environmental human rights defenders (EHRDs) based on the Declaration+25, a supplement to the UN Declaration on Human Rights Defenders, and a joint submission in partnership with the Center for International Environmental Law, Earthjustice, FIAN International, the Global Initiative for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, Human Rights Watch and Oxfam.
‘States parties should respect, protect, and promote the work of environmental and indigenous human rights defenders, as well as other civil society actors who support people in marginalized and disadvantaged situations in realizing their Covenant rights.’ States parties should take all necessary measures to ensure that environmental human rights defenders and journalists can carry out their work, without fear of harassment, intimidation or violence, including by protecting them from harm by third parties.’
ISHR welcomes that priorities from the joint NGO submission to the CESCR are reflected in the General Comment, in particular Indigenous Peoples’ right to ‘free, prior and informed consent’ and the need to transition away from fossil fuels (including by reducing ineffective subsidies).
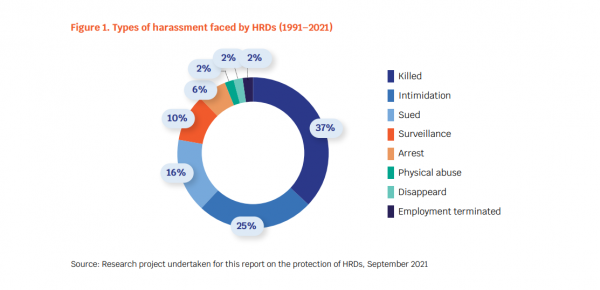
However, we regret that the Comment does not more explicitly acknowledge the critical role of EHRDs in promoting sustainable development or strategic lawsuits against public participation (SLAPPs) as an obstacle to their engagement. The CESCR has previously noted the risks faced by HRDs and provided guidance on their recognition and protection in the context of land issues in General Comment No. 26 and it should have extended this analysis to EHRDs in the context of sustainable development. The use of SLAPPs to silence HRDs has been acknowledged by other UN bodies, including in the most recent report of the Special Rapporteur on the Situation of Human Rights Defenders, Ms. Mary Lawlor, to the Third Committee of the General Assembly.
Some additional highlights from the General Comment are set out below.
- The Committee found that ‘[t]he full realization of Covenant rights demands a just transition towards a sustainable economy that centres human rights and the well-being of the planet’.
- States should supervise commercial activity, establish a legal obligation for businesses in respect of environment and human rights due diligence, and ensure that victims of human rights violations stemming from businesses have redress.
- States have obligations to conduct human rights and environmental impact assessments, which are to be undertaken with ‘meaningful public participation’.
- States have an extraterritorial obligation to ensure that any activities within the State or in areas under its control do not substantially adversely affect the environment in another country. This also extends to preventing businesses in the State from causing such harm in another jurisdiction. Even though the CESCR does not expressly mention it in the Comment, this should also apply to cases of attacks against EHRDs.
- The CESCR also clarifies States’ obligations towards marginalized communities, spotlighting the concept of intersectionality. It also explicitly notes that equal exercise of economic, social and cultural rights by women and men is a prerequisite for sustainable development, encouraging States to redistribute the unpaid domestic work undertaken by women and girls.
- Environment-related obligations have also been set out for States in the context of specific Covenant rights, for example, the right to self-determination , right to freely utilize natural resources , right to work , right to an adequate standard of living, right to the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health, right to education and other economic, social and cultural rights.
- The General Comment recognises that certain communities are particularly vulnerable to the effects of environmental degradation – it calls on States to identify and protect those at risk. The CESCR focuses particularly on children (specifically calling for child rights defenders to be recognised and protected and for their participation in climate action to be facilitated), Indigenous Peoples, peasants, pastoralists, fishers and others in rural areas, and displaced persons.
‘Environmental degradation, including climate change, intensifies the vulnerabilities of individuals and groups who have historically experienced and/or experience marginalization. These vulnerabilities are shaped by intersecting factors such as socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, gender, disability, age, migratory status, sexual orientation, and gender identity.’