A new report by the research organization Swedwatch of 29 April 2025 highlights critical human rights risks associated with the global transition to renewable energy. The report reveals that human rights and environmental defenders face serious threats and reprisals in countries where renewable energy projects are being rapidly developed.
More than half of the world’s total prospective wind farm capacity, and more than two thirds of the prospective solar farm capacity, is estimated to take place in countries with obstructed, repressed or closed civic space.
While scaling up wind, solar, and hydropower is essential to limiting global warming to 1.5°C, this growth must not come at the expense of human rights.
–We cannot build a green future on the backs of those who are silenced or displaced. The renewable energy transition must not come at the cost of human rights. Defenders are not obstacles – they are essential allies in ensuring that this is just, equitable, and sustainable, says Alice Blondel, Director Swedwatch.
Renewable energy projects require large land areas, often affecting local communities, ecosystems, and livelihoods. Swedwatch’s analysis shows that the renewable energy transition will largely take place in countries with restricted civic space and poor human rights protections, where defenders who raise concerns often face harassment, legal persecution and at times even deadly violence.
The report Renewables and Reprisals – Defenders at risk in the green energy transition in Brazil, Honduras, Mozambique, and the Philippines is based on a global mapping of such high-risk areas for defenders, where civic space is restricted and where renewable energy expansion is projected to accelerate. Additionally, the report presents four case studies from Mozambique, Honduras, Brazil, and the Philippines, where defenders and affected community members describe restrictions and reprisals of defenders linked to renewable energy projects.
The report is authored by Swedwatch with input from Terramar Institute (Instituto Terramar), Network of Women Human Rights Lawyers and Defenders (Red de Abogadas Defensoras de Derechos Humanos) and Jalaur River for the People’s Movement (JRPM).
-The report underscores the urgent need for stronger protections for defenders, transparent consultation processes, and corporate accountability. Without immediate action, the rapid expansion of renewables risk repeating the same human rights abuses seen in industries such as mining and agribusiness, rather than fostering a truly just energy transition, says Alice Blondel.
Expansion of renewables in countries with high risks for defenders
Swedwatch’s findings indicate that a large share of the expansion of renewable energy is taking place in countries where civic space is restricted, and defenders are at significant risk.
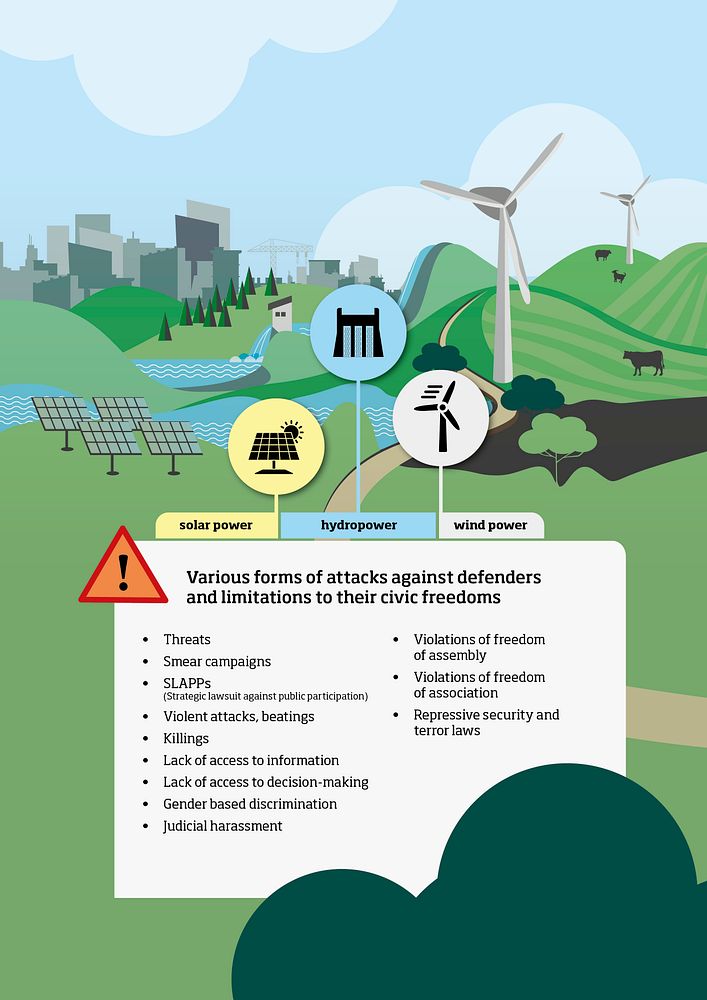
Case studies: Defenders under threat
In the four case studies, defenders from Mozambique, Honduras, Brazil and the Philippines described restrictions of basic civic freedoms and risks of verbal, legal or violent physical attacks when reporting about impacts of renewable energy projects.
Mozambique: According to interviews in the report, the planning of the Mphanda Nkuwa hydropower project has been marred by inadequate social and environmental impact assessments, lack of transparency, and suppression of civic engagement. Defenders reported threats, violation of freedom of assembly, and an overall disregard for their right to participate in decision-making processes.
Honduras: Human rights defenders have faced legal intimidation through SLAPPs (Strategic Lawsuits Against Public Participation) for their criticism of the Los Prados solar power project, according to a group of women human rights lawyers. Community members involved in protests have allegedly been surveilled and subjected to repressive actions by security forces. Defenders also reported smear campaigns in the media, further restricting their ability to voice concerns.
Brazil: In Brazil, the wind power project Bons Ventos failed to properly include impacted communities, including marginalized groups, traditional fishing, and quilombola communities, in consultations, according to interviews. Defenders decided to remain anonymous in the interviews out of fear of reprisals, citing increasing threats and violence against defenders in the past years.
The Philippines: Indigenous defenders from the Tumandok communities were allegedly threatened, harassed, and killed when the national police and the armed forces raided their communities after community leaders criticized the Jalaur River Multipurpose project, according to a CSO operating in the area. Defenders reporting on the dam project outlined persecution, surveillance and red-tagging – terror-labelling by the government accusing defenders of being communist insurgents, creating an environment of fear and impunity.
Swedwatch´s recommendations
As the world races to meet climate targets, a just transition must include the voices of those most affected by energy projects, and defenders are essential in ensuring that renewable energy projects respect human rights and the environment.
-Governments, businesses, and financial institutions must work together to ensure that human rights are protected, and that defenders can operate without fear of repression or violence. Engaging with defenders as valuable partners rather than as adversaries can help governments and businesses ensure renewable energy projects’ alignment with international human rights obligations, mitigate conflicts, and promote sustainable development, says Jessica Johansson.
Detailed recommendations to different actors can be found in the report, below the main ones are summarized:
Recommendations for governments:
- Adopt legislation on mandatory human rights due diligence (HRDD) for companies, highlighting risks to defenders and meaningful consultation with defenders.
- Adopt laws on company transparency laws and access to information.
- Establish and enforce protections for defenders, ensuring they can operate without fear of retaliation, and provide effective legal remedies for those affected by violations.
Recommendations for companies and investors:
- Strengthening their HRDD processes by integrating civic space risks and ensuring meaningful stakeholder engagement with defenders.
- Adopt and enforce a zero-tolerance policy against reprisals targeting defenders (and affected communities).
- Take appropriate action when business partners or third parties commit violations in relation to their business activities.







