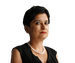Women dressed as the mothers and grandmothers of the Plaza de Mayo gather in Buenos Aires, Argentina, in March. Photograph: Rodrigo Abd/AP
On Wednesday 6 August 2025 the Guardian carried an interview with Buscarita Roa, one of the last of the Abuelas.” ..
Argentina’s 1976-83 military dictatorship tortured, killed and “disappeared” an estimated 30,000 people – political opponents, students, artists, union leaders: anyone it deemed a threat. Hundreds of babies were also taken, either imprisoned with their parents, or given to military families. The Abuelas de Plaza de Mayo have fought for almost 50 years to find these grandchildren. Buscarita Roa is one of two surviving active members.
On 28 November 1978, my 22-year-old son, José, his wife, Marta, and their baby daughter, Claudia, joined the list of those “disappeared”. A squad of Argentina’s military police stormed their home and I couldn’t find out any more. I went everywhere to look for them – police stations, courthouses, army camps, churches. I was desperate. But nobody would answer me. Every door was closed. It was a suffocating, hermetic time.
Then one day, not long after they were taken, I watched as a group of women walked in circles around the Plaza de Mayo in Buenos Aires. These mothers and grandmothers had started to gather, demanding answers about their missing relatives. I recognised one of the women. She said come with us, and I did.
We – who would become known as the Abuelas – didn’t know each other before. But we would meet every week and walk round and round the square, identifying each other with our white headscarves.
At first some of the husbands came, but we knew they risked being “disappeared” too, so then the men stayed at home and we went alone. It was still dangerous, a terrifying time, and some of the first mothers were taken themselves.
When the police ordered us to leave, and we didn’t, they charged at us on horseback. But we were younger then, so we could run.
Together we started going to the police stations and the courts, searching for answers. We cried in front of them, and they told us to go away, they didn’t want to see us. We knew the dictatorship was watching us from afar.skip past newsletter promotion
My granddaughter’s disappearance haunted my life. She was only eight months old when she was taken, and whenever I would see a little girl who looked like her, I would follow her, unable to stop until I saw her face. If there were people at my front door I would think, oh she must have come home. Other times, people would tell us they had seen a neighbour with a new baby. So we would go to their houses, trying to glimpse the child, to see if they looked like one of ours. We were doing crazy, desperate things, but it was all we had.
Many years passed before we started to receive any information. Most people didn’t believe us, and those that did thought our sons were terrorists. Still, we continued to go to Plaza de Mayo to pray for the return of our children. And when the country’s economic situation improved, we started travelling abroad to share our story too.
In 2000, I found my granddaughter, and was able to hug her again for the first time in two decades. People had come forward with their suspicions, and a judge agreed to investigate. We learned that Claudia had been taken to the clandestine detention centre “El Olimpo” with her mother, where she was kept for three days before being illegally adopted by a military family. They created a fake birth certificate, signed by a military doctor. My son and daughter-in-law were tortured and killed.
Claudia was in my heart every day that she was missing. I can’t explain what I felt when I found her. It was a pure, overwhelming joy. But I was also afraid, fearful that she would reject me. By then she was 21, and had been raised by a military family. I couldn’t invade my granddaughter’s life just like that, she needed to figure out the terrible truth and start trusting us. Slowly, over long afternoons of mate [a traditional herbal drink], we got to know each other and have built a beautiful relationship.
Belonging to the Abuelas helped me to heal. We laughed, we cried and we became friends. We were relentless too – we women have not rested once in half a century. But while some of us found our grandchildren, others only found bodies, and most of us found nothing at all. And then there is the battle of time; it is cruel and many of the Abuelas have died. There were once many of us, and now there are fewer than 10.
Estela de Carlotto, the president of the Abuelas, and I are the two last active members. But we are growing old too, and I don’t know how much further life will take us. We have found 140 of the grandchildren, with the last reunited last month, but we estimate that nearly 300 are still missing.
The ones we have found have now taken up the mantle. This is the legacy de Carlotto and I leave behind: a generation of grandchildren still looking for the others.
My lifelong work has consisted of searching for my son and daughter-in-law. I am 87 years old now, but I will never give up.
As told to Harriet Barber