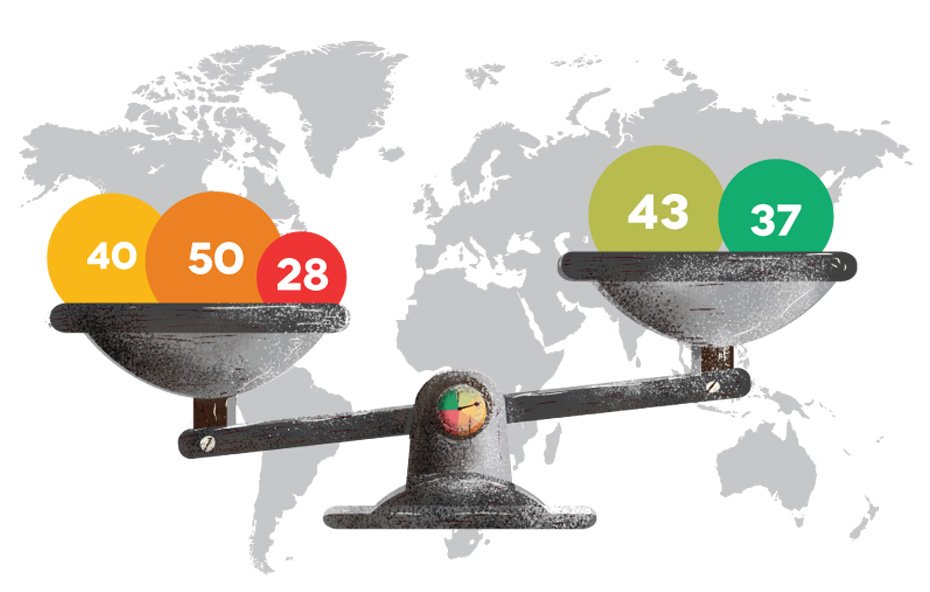
On 21 March 2024, Nikkei Asia carried the story on Kyrgyzstan taking a page from Russia in pushing for a ‘foreign agents’ law

Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov faces a high-stakes decision on whether to sign new legislation that critics warn will significantly impair how human rights defenders and independent media, among others, can work in his mountainous Central Asian state. On March 14, Kyrgyzstan’s parliament voted overwhelmingly in favor of a “foreign agents” bill that mirrors legislation adopted in Russia over a decade ago. The law is designed to control the activities of nonprofit and nongovernmental organizations that receive funding from abroad by compelling them to register as “foreign representatives,” leading to closer scrutiny of their activities by the authorities.
Japarov has a month from that date to sign it into law. Many observers have been vocal in their opposition and are urging the president to veto the bill. Syinat Sultanalieva, Central Asia researcher at Human Rights Watch, told Nikkei Asia that this law “would see the further and sharper shrinking of civil society,” a sector that has been under attack in Kyrgyzstan for more than a decade. BUT see: https://www.aol.com/kyrgyzstan-adopts-law-targeting-foreign-100124498.html
In the meantime the Prague based NGO, People in Need, speaks out against the Slovakian government’s proposed measures to curb critical media and NGOs, which would mirror tactics employed by autocrats and dictators in places ranging from Russia to Latin America, It has raised concerns about the erosion of civil liberties and the stifling of dissent. In a move reminiscent of authoritarian regimes, officials seek to designate these entities as “foreign agents,” a term often utilised to suppress opposition voices. The Fico government has already taken steps to cut NGO funding, raising further alarms about the independence of civil society activities. Additionally, Culture Minister Martina Šimkovičová and Justice Minister Boris Susko have initiated cuts to subsidy programmes, redirecting funds away from NGOs to other areas, citing concerns about transparency and favouritism in grant allocation. The government’s actions have prompted backlash from NGOs, with 90 organisations signing a petition against the minister’s decisions.
As an organisation with roots steeped in the freedom and civic movements of post-Cold-War Czechoslovakia, we are appalled to see the illiberal turn taken by the Slovak government. The Fico government’s proposal to impose a Russian-style foreign agents’ law is anathema to the shared goals of the Czech and Slovak people who fought to end the Russian subjugation of our homelands. This is of great concern and sadness to us at People in Need.
https://www.peopleinneed.net/slovak-government-targets-ngos-with-proposed-foreign-agents-act-11299gp
On 21 March 2024, a large group of civil society organisations jointly called on the president of Kyrgyzstan, Sadyr Japarov, to veto the amendments to the Law on Non-commercial Organisations, known as the law on ‘foreign representatives’ which clearly violates the country’s international human rights obligations and would be a devastating blow the civil society. [see also: https://humanrightsdefenders.blog/tag/foreign-agent-law/]
…We are writing to you on behalf of the undersigned civil society organisations from different countries to express support for Kyrgyzstan’s civil society and urge you to veto the amendments to the Law on Non-commercial Organisations, known as the law on ‘foreign representatives’, which parliament adopted on third reading on 14 March 2024. The proposed amendments fall seriously short of Kyrgyzstan’s international human rights obligations and risk delivering a devastating blow to its vibrant civil society. The amendments will impair civil society’s ability to carry out its important and legitimate work to the benefit of the people of Kyrgyzstan, and to promote public participation, transparency, accountability and good governance, thereby eroding democratic and human rights progress made by Kyrgyzstan with negative implications for its international reputation. Further, the proposed amendments will endanger international development and economic assistance programmes in the country, which will also undermine prospects for the achievement of sustainable development goals contrary to your government’s ambitious agenda in this area. Thus, we urge you to veto the amendments for the benefit of Kyrgyzstan and its people.
Both national and international human rights experts have concluded that the draft law on ‘foreign representatives’ clearly violates Kyrgyzstan’s international human rights obligations. For example, such conclusions were presented in a joint communication addressed to your government by three UN Special Rapporteurs, appointed by the UN Human Rights Council, of which Kyrgyzstan currently is a member. The three rapporteurs stated: ‘many provisions in the proposed law would be contrary to the international human rights obligations of the Kyrgyz Republic, including the right to the freedom of association, the right to freedom of opinion and expression, the right to non-discrimination and the right to privacy. If passed, this draft law could have a chilling effect on the operation of all associations in the Kyrgyz Republic, limiting their ability to advocate for human rights, provide social services, and contribute to the development of a robust and inclusive society.’
In an earlier legal assessment prepared at the request of Kyrgyzstan’s Ombudsperson, the OSCE Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR) found that the proposed provisions lack legitimate justification and do not meet the requirements of international human rights law for acceptable restrictions on the right to freedom of association. ODIHR also stressed that the key concepts of ‘foreign representatives’ and ‘political activities’ used in the draft law are inconsistent with the principle of legal certainty and predictability and ‘would allow unfettered discretion on the part of the implementing authorities’. ODIHR further found that the proposed provisions are contrary to the principle of non-discrimination and risk stigmatising organisations carrying out legitimate work and triggering mistrust, fear and hostility against them.
The draft law on ‘foreign representatives’ does not only violate your country’s international obligations but also contradicts provisions of the Constitution of the Kyrgyz Republic (including articles 36, 32, 24 and 29), which protect the right to freedom of association and other fundamental rights. In this way, the draft law challenges the legitimacy of the current Constitution, which was initiated by you and endorsed by citizens in a national referendum in 2021.
The proponents of the draft law on ‘foreign representatives’ have argued that it is aimed at ensuring the transparency of civil society organisations (CSOs). However, while transparency is an important issue, it is not a legitimate reason under international human rights law for imposing invasive, discriminatory, and stigmatising restrictions on CSOs. On the contrary, transparency can be ensured in ways that do not contradict international law nor hamper the work of CSOs. Moreover, all non-commercial organisations in Kyrgyzstan, including those that receive foreign funding, are already subjected to extensive state control and regularly report about their activities and finances to various state bodies, which ensures transparency of their work. In particular, amendments to the Law on Non-commercial Organisations, adopted in 2021, oblige non-commercial organisations to annually provide detailed information on their sources of funding, use of funds and assets for publication on the Tax Service’s website. This information is thus already publicly accessible.
Rather than increasing the transparency of non-commercial organisations, the draft law risks undermining civil society’s crucial role in assisting public bodies with the provision of support to vulnerable groups of the population, and also in promoting public sector transparency and accountability. Watchdog organisations have already warned of a significant decline in government transparency in Kyrgyzstan, preventing the exposure of wrongdoing and increasing the risk of corruption. This impairs foreign investments as well as economic growth and well-being in the country.
Kyrgyzstan’s international partners have warned that the adoption of the law on ‘foreign representatives’ would negatively affect development assistance programmes in the country. For example, in a joint statement issued on 14 March 2024, the Delegation of the EU to the Kyrgyz Republic and the Embassies of Canada, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and the United States stated that the proposed provisions would ‘jeopardise our ability to provide assistance that improves the lives of the citizens and residents of the Kyrgyz Republic’. They stated that, if signed in its current form, the law ‘has the potential to hurt the most vulnerable who rely on the essential services – such as food, healthcare, and education – that non-profits and NGOs [non-governmental organisations] provide’. The UN Resident Coordinator in the Kyrgyz Republic pointed out that enacting the law would threaten civil society engagement in development initiatives and the achievement of UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Thus, the law contradicts the government’s aim of being among the top 30 countries in the realisation of SDGs by 2030.
The World Bank and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development have also stressed the importance that they attach to CSO engagement for the success of their in-country operations, when commenting on NGO concerns about the draft law’s potential impact on the activities of international financial institutions in Kyrgyzstan.
As you know, as a beneficiary of the General Scheme of Preferences Plus (GSP+), the Kyrgyz Republic is required to effectively implement international human rights conventions, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) in return for trade benefits afforded by the EU. Thus, the adoption and enforcement of the law on ‘foreign representatives’ is likely to negatively affect these benefits. The European Commission’s recent GSP+ monitoring report on the Kyrgyz Republic highlighted shrinking space for civil society as a key area of concern and called for swift measures to reverse this negative trend in the light of the country’s ICCPR obligations. Moreover, in its resolution adopted in July 2023, the European Parliament called for a reassessment of Kyrgyzstan’s GSP+ benefits in view of recent developments, in particular draft legislation that runs counter to the country’s international human rights obligations.
We are aware that proponents of the draft law on ‘foreign representatives’ have argued that it is similar to the US Foreign Agent Registration Act (FARA). However, FARA differs from the proposed legislation in Kyrgyzstan in crucial respects. In particular, FARA is not targeted at non-commercial organisations that receive foreign funding. Instead, FARA requires persons who conduct certain activities ‘at the order’ or ‘under the direction or control’ of a foreign government or other foreign entity to register as an ‘agent of a foreign principal’ and periodically file supplementary information about their activities in this capacity. The purpose of FARA is to ensure the public disclosure of such information rather than to subject those registered under it to ongoing, invasive state control.
President Japarov, when you consider whether or not to sign the draft law on ‘foreign representatives’, you are deciding the fate of civil society in Kyrgyzstan. Will you opt for the path taken by authoritarian countries, where similar legislation has been used in campaigns to systematically dismantle independent civil society, with negative implications for the reputation, prosperity and well-being of these countries? Or for a more forward-looking, inclusive, and democratically-oriented approach under which CSOs are treated as important, respected partners who can work together with state bodies in addressing societal problems, and international partners retain their confidence in Kyrgyzstan’s commitment to sustainable development?
For the reasons outlined above, we urge you to refrain from signing the draft law on ‘foreign representatives’ and ensure that any new legislation impacting non-commercial organisations reflects Kyrgyzstan’s international human rights obligations and undergoes thorough and inclusive consultations with civil society, as well as national and international experts. When elaborating this type of legislation, it is crucial to take the opinions of CSOs directly affected by it into account.
Signed by the following organisations (listed in the order of signature):
International Partnership for Human Rights (IPHR), Belgium
IDP Women Association Consent, Georgia
Norwegian Helsinki Committee
Hungarian Helsinki Committee, Hungary
Legal Policy Research Centre, Kazakhstan
Public Association “Dignity”, Kazakhstan
Netherlands Helsinki Committee
Civil Rights Defenders, Sweden
Protection of Rights without Borders NGO, Armenia
Swedish OSCE-network
Helsinki Citizens’ Assembly – Vanadzor, Armenia
Center for Civil Liberties, Ukraine
Public Verdict, Russia
Turkmen Helsinki Foundation, Bulgaria
Crude Accountability, USA
Freedom Files, Poland
Human Rights Center “Viasna”, Belarus
Center for Participation and Development, Georgia
Human Rights Defence Center Memorial, Russia
Civic Assistance Committee, Russia
Austrian Helsinki Association
Bulgarian Helsinki Committee
Human Rights Center (HRC), Georgia
Macedonian Helsinki Committee
Sova Research Center, Russia
Promo LEX Association, Moldova
Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights, Poland
ARTICLE 19 Europe
FIDH (International Federation for Human Rights), within the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT), within the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
Amnesty International
https://asia.nikkei.com/Politics/Kyrgyzstan-takes-page-from-Russia-in-pushing-foreign-agents-law